what does the body use to build maintain and repair cells quizlet
An Introduction to the Human Body
Functions of Human Life
Learning Objectives
By the cease of this section, yous volition be able to:
- Explain the importance of arrangement to the role of the man organism
- Distinguish between metabolism, anabolism, and catabolism
- Provide at least 2 examples of human responsiveness and human movement
- Compare and contrast growth, differentiation, and reproduction
The different organ systems each have different functions and therefore unique roles to perform in physiology. These many functions can be summarized in terms of a few that we might consider definitive of homo life: organisation, metabolism, responsiveness, motion, evolution, and reproduction.
Organization
A human body consists of trillions of cells organized in a way that maintains distinct internal compartments. These compartments continue trunk cells separated from external environmental threats and keep the cells moist and nourished. They also separate internal body fluids from the countless microorganisms that abound on body surfaces, including the lining of certain passageways that connect to the outer surface of the body. The intestinal tract, for example, is home to more than bacterial cells than the full of all human cells in the body, yet these bacteria are outside the body and cannot be allowed to broadcast freely inside the body.
Cells, for example, take a jail cell membrane (also referred to equally the plasma membrane) that keeps the intracellular environment—the fluids and organelles—split up from the extracellular surroundings. Blood vessels keep claret inside a closed circulatory arrangement, and nerves and muscles are wrapped in connective tissue sheaths that separate them from surrounding structures. In the chest and abdomen, a diversity of internal membranes keep major organs such every bit the lungs, heart, and kidneys dissever from others.
The body'southward largest organ system is the integumentary organisation, which includes the peel and its associated structures, such as pilus and nails. The surface tissue of skin is a barrier that protects internal structures and fluids from potentially harmful microorganisms and other toxins.
Metabolism
The first law of thermodynamics holds that energy tin neither be created nor destroyed—information technology can only change grade. Your basic function as an organism is to swallow (ingest) energy and molecules in the foods you lot eat, catechumen some of it into fuel for movement, sustain your torso functions, and build and maintain your body structures. At that place are two types of reactions that accomplish this: anabolism and catabolism.
- Anabolism is the process whereby smaller, simpler molecules are combined into larger, more circuitous substances. Your trunk tin can gather, by utilizing energy, the complex chemicals it needs past combining small molecules derived from the foods yous eat
- Catabolism is the process by which larger more than complex substances are cleaved downwardly into smaller simpler molecules. Catabolism releases energy. The complex molecules establish in foods are cleaved down then the torso can use their parts to get together the structures and substances needed for life.
Taken together, these two processes are chosen metabolism. Metabolism is the sum of all anabolic and catabolic reactions that take place in the body ((Figure)). Both anabolism and catabolism occur simultaneously and continuously to keep you alive.
Metabolism
Anabolic reactions are building reactions, and they swallow energy. Catabolic reactions break materials down and release free energy. Metabolism includes both anabolic and catabolic reactions.
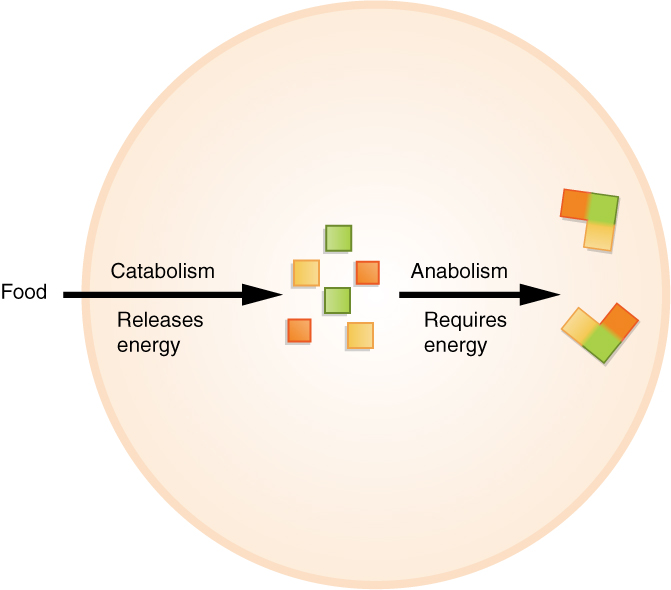
Every cell in your torso makes employ of a chemic compound, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), to shop and release energy. The cell stores energy in the synthesis (anabolism) of ATP, then moves the ATP molecules to the location where free energy is needed to fuel cellular activities. And so the ATP is cleaved down (catabolism) and a controlled amount of energy is released, which is used by the cell to perform a particular chore.
View this animation to learn more about metabolic processes. Which organs of the body likely acquit out anabolic processes? What about catabolic processes?
Responsiveness
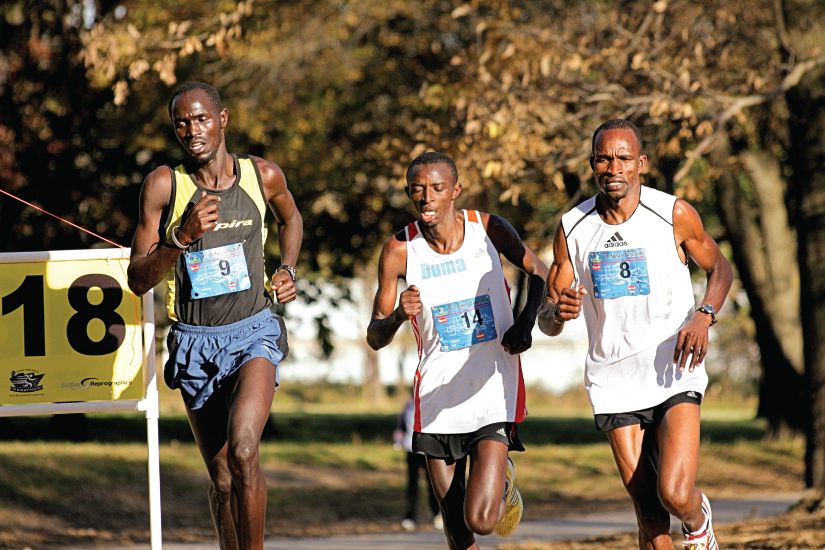
Responsiveness is the power of an organism to conform to changes in its internal and external environments. An example of responsiveness to external stimuli could include moving toward sources of food and water and away from perceived dangers. Changes in an organism's internal environment, such as increased body temperature, tin can crusade the responses of sweating and the dilation of claret vessels in the skin in order to decrease body temperature, as shown by the runners in (Figure).
Movement
Human being motility includes not but deportment at the joints of the body, but also the motion of individual organs and fifty-fifty individual cells. As you read these words, carmine and white blood cells are moving throughout your torso, muscle cells are contracting and relaxing to maintain your posture and to focus your vision, and glands are secreting chemicals to regulate body functions. Your body is coordinating the action of entire muscle groups to enable you to movement air into and out of your lungs, to push claret throughout your torso, and to propel the nutrient you have eaten through your digestive tract. Consciously, of course, you contract your skeletal muscles to motion the bones of your skeleton to become from i place to some other (as the runners are doing in (Figure)), and to bear out all of the activities of your daily life.
Marathon Runners
Runners demonstrate two characteristics of living humans—responsiveness and motion. Anatomic structures and physiological processes allow runners to coordinate the activeness of muscle groups and sweat in response to rising internal body temperature. (credit: Phil Roeder/flickr)

Development, growth and reproduction
Development is all of the changes the body goes through in life. Evolution includes the process of differentiation, in which unspecialized cells become specialized in structure and function to perform certain tasks in the body. Development besides includes the processes of growth and repair, both of which involve cell differentiation.
Growth is the increase in trunk size. Humans, like all multicellular organisms, abound by increasing the number of existing cells, increasing the amount of non-cellular textile around cells (such equally mineral deposits in os), and, within very narrow limits, increasing the size of existing cells.
Reproduction is the germination of a new organism from parent organisms. In humans, reproduction is carried out past the male and female reproductive systems. Considering death will come to all complex organisms, without reproduction, the line of organisms would end.
Chapter Review
Most processes that occur in the human body are not consciously controlled. They occur continuously to build, maintain, and sustain life. These processes include: arrangement, in terms of the maintenance of essential trunk boundaries; metabolism, including free energy transfer via anabolic and catabolic reactions; responsiveness; movement; and growth, differentiation, reproduction, and renewal.
Interactive Link Questions
View this animation to learn more about metabolic processes. What kind of catabolism occurs in the heart?
Review Questions
Metabolism can be divers as the ________.
- aligning by an organism to external or internal changes
- procedure whereby all unspecialized cells become specialized to perform distinct functions
- process whereby new cells are formed to replace worn-out cells
- sum of all chemical reactions in an organism
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an important molecule considering it ________.
- is the result of catabolism
- release energy in uncontrolled bursts
- stores energy for use by body cells
- All of the to a higher place
Cancer cells can be characterized equally "generic" cells that perform no specialized torso function. Thus cancer cells lack ________.
- differentiation
- reproduction
- responsiveness
- both reproduction and responsiveness
Disquisitional THINKING QUESTIONS
Explicate why the smell of smoke when y'all are sitting at a campfire does non trigger warning, only the smell of fume in your residence hall does.
When yous are sitting at a bivouac, your sense of odour adapts to the smell of smoke. Just if that smell were to suddenly and dramatically intensify would you exist probable to notice and respond. In contrast, the smell of fifty-fifty a trace of fume would be new and highly unusual in your residence hall, and would be perceived as danger.
Identify three different ways that growth tin can occur in the human torso.
Growth tin occur past increasing the number of existing cells, increasing the size of existing cells, or increasing the corporeality of non-cellular material around cells.
Glossary
- anabolism
- assembly of more than complex molecules from simpler molecules
- catabolism
- breaking downward of more complex molecules into simpler molecules
- evolution
- changes an organism goes through during its life
- differentiation
- process by which unspecialized cells become specialized in structure and function
- growth
- procedure of increasing in size
- metabolism
- sum of all of the body'southward chemical reactions
- renewal
- process by which worn-out cells are replaced
- reproduction
- process by which new organisms are generated
- responsiveness
- power of an organisms or a arrangement to accommodate to changes in conditions
bucklandwommant88.blogspot.com
Source: https://opentextbc.ca/anatomyandphysiologyopenstax/chapter/functions-of-human-life/
0 Response to "what does the body use to build maintain and repair cells quizlet"
Post a Comment